Case Studies: Successful Urban Microforests and Biodiversity Outcomes
Chosen theme: Case Studies: Successful Urban Microforests and Biodiversity Outcomes. Explore real-world projects transforming tiny urban plots into thriving biodiversity hotspots. Read, respond, and subscribe to follow new successes, lessons learned, and replicable methods.

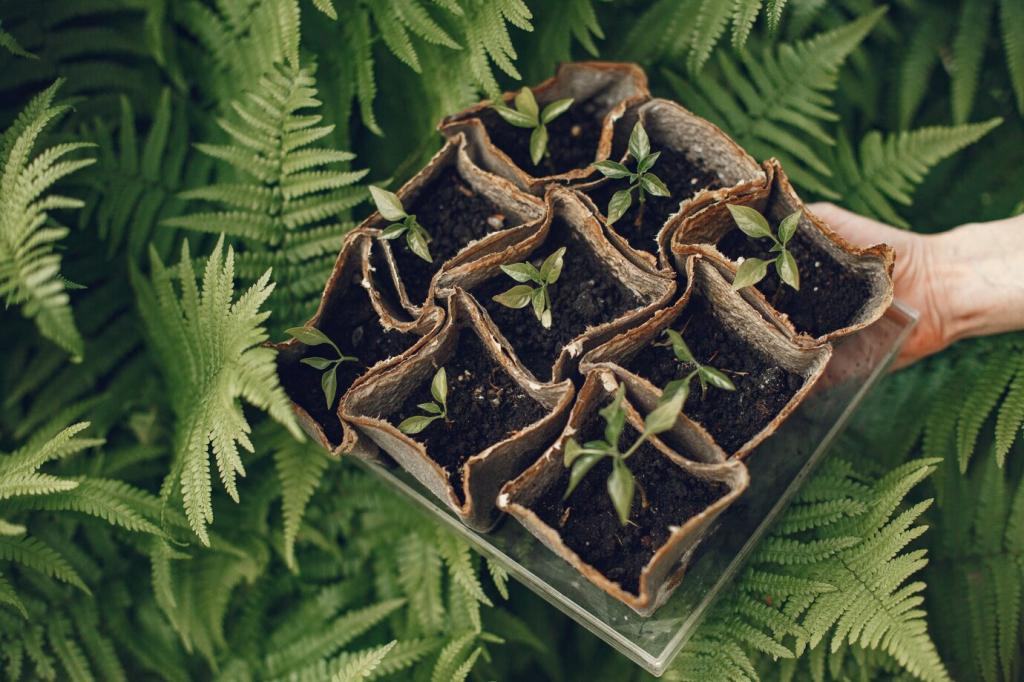
Year One: Soil, Shelter, and Survival
In the first twelve months, teams focus on soil structure, mulch blankets, and frequent watering. Survival improves dramatically when windbreaks protect seedlings and neighbors commit regular, light maintenance and cheerful weekend check-ins.
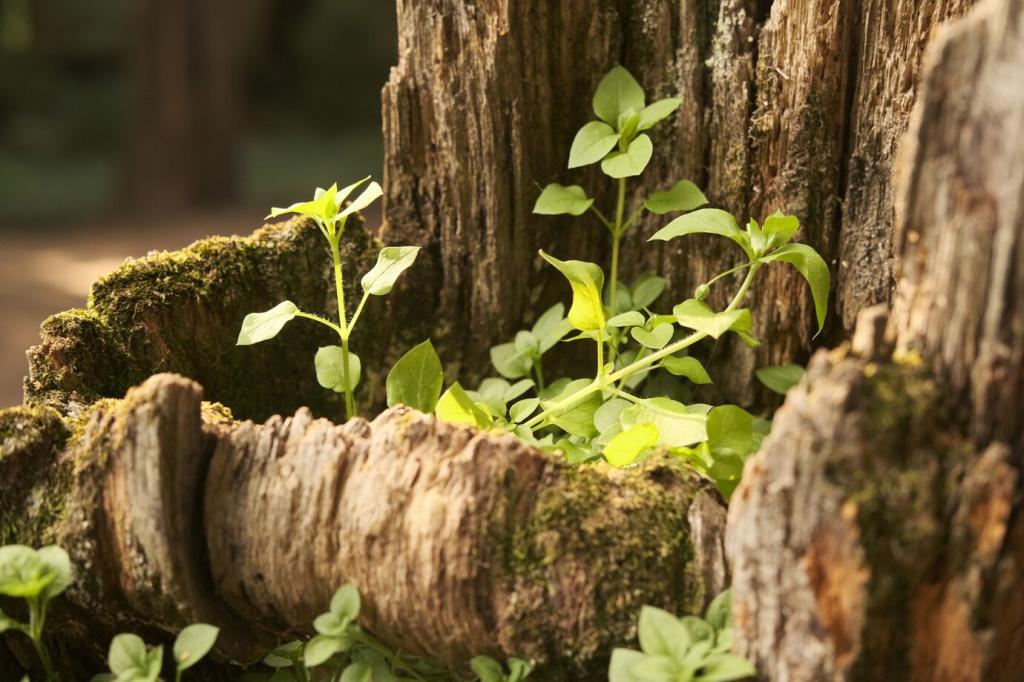

Year Three: Shade Arrives, Species Bloom
By year three, canopy layers start knitting together, humidity rises, and leaf litter accumulates. Pollinators concentrate at flowering edges, while lizards, beetles, and small birds establish reliable daily pathways between water, nectar, and cover.
Year Five: A Self-Sustaining Neighborhood Refuge
Maintenance drops to seasonal pruning and occasional mulching. Citizen scientists record stable nesting, increased native regeneration, and cooler microclimates that spill beyond the forest edge into streets, courtyards, and bus stops waiting in shade.
Successful teams map historic vegetation and modern pressures, then choose locally native species for every layer. Matching shrubs, understory trees, and canopy to soil and light conditions reduces failure, diversifies habitat niches, and stabilizes seasonal resources.
Methods That Made It Work
Tight spacing encourages upward growth, early shade, and moisture retention. Within two seasons, weeds diminish, fungal networks expand, and insect guilds multiply across niches that once baked under exposed, compacted ground beside footpaths and walls.
Methods That Made It Work
Biodiversity Outcomes You Can Measure
Teams run short timed counts along fixed paths, noting bees, butterflies, and hoverflies per flowering patch. Results show steep increases by the second year, especially where staggered blooms provide continuous nectar through spring, summer, and early autumn.
Biodiversity Outcomes You Can Measure
Volunteers record calls at dawn, mark nesting attempts, and map perches. As shrubs thicken, predation risk drops, species richness climbs, and fledglings use layered vegetation to move safely between food, water, and neighboring green corridors.

Places That Inspire: Compact Sites, Big Returns
A wind-scoured playground adopted a dense native mix along its fence. Within three years, teachers reported quieter recess, deeper shade, and frequent monarch visits that sparked student-led pollinator gardens and lunch break observation clubs.
Places That Inspire: Compact Sites, Big Returns
Beside a busy line, residents planted thickets that stitch habitat between parks. Hedgehogs, skinks, and night-flying moths now traverse a safe corridor where ballast, litter, and noise once defined an inhospitable, overlooked strip.


Saturday Circles and Ritual Check-Ins
Volunteers gather monthly for short tasks, tea, and updates. Predictable rhythms prevent burnout, new neighbors learn skills quickly, and children claim roles like mulching captain or worm scout with unstoppable curiosity and pride.
Citizen Science as Community Glue
Simple monitoring becomes conversation. People swap bird notes, upload photos, and compare seasons, transforming data collection into friendship that keeps watering cans moving and commitments steady when weather turns difficult or schedules tighten.
Anecdote: The Bench That Started Conversations
A single salvaged bench invited lingering. One elder recalled pre-pavement creeks, inspiring teenagers to map historical streams and propose a microforest chain that follows buried waters across alleys, courtyards, and overlooked municipal corners.
Design Lessons to Replicate Elsewhere
Design edges with plant variety, nectar succession, and interpretive signs. Busy boundaries host crucial forage while signaling care, inviting passersby to linger, ask questions, and potentially join future planting days with neighbors.
Design Lessons to Replicate Elsewhere
Stack shrubs, understory, and canopy with logs, stones, and leaf piles. These microhabitats shelter decomposers, amphibians, and insects, strengthening food webs and buffering the site during heatwaves, downpours, and unexpected cold snaps.


Challenges and Honest Reflections
Drought, Heat, and Emergency Water Plans
Mulch depth, shade cloth, and water totes on wheels made the difference during a heatwave. Afterwards, teams codified triggers for emergency watering and adopted morning checks to prevent midday stress and needless losses.
Balancing Wildness with Urban Expectations
Some neighbors feared mess or pests. Projects responded with tidy edges, seasonal mowing of path margins, and regular storytelling that reframed fallen leaves as habitat, not neglect, while celebrating visible signs of care.
Security, Vandalism, and Careful Visibility
A few sites lost saplings. Replacements paired with small fences, motion lights, and community art reduced damage, while newsletters celebrated helpers by name, deepening pride and making misuse socially unacceptable within the block.
Stay Involved: Share, Subscribe, and Collaborate
Send a short story, photos, and any monitoring notes. We will feature selected submissions, compare methods, and invite you to a live session where peers trade tips, celebrate wins, and troubleshoot stubborn challenges together.